Business Analytics vs. Data Analytics: Which is Better?
- October 11, 2023
- Posted by: Taxila Editor
- Category: blog
Data plays such a significant role in this world of digitization. According to the research, 328.77 million terabytes of data are developed each day by technological breakthroughs and ubiquitous computing. It is anticipated that this will grow exponentially as we access internet-connected devices, and produce & store information.
As large amounts of data are being produced, it is important to harness this information by learning how to use these data to make better decisions. Due to these emerging trends, data analytics and business analytics professionals are in demand. In every industry, their role has emerged because they help in managing qualitative and quantitative data for generating business insights.
Business Analytics and Data Analytics are two interrelated fields that are essential in analyzing data to make informed decisions. Both fields are used for managing the power of data, but they serve different goals and have different approaches and uses.
Business Analytics helps businesses identify problems, opportunities, and solutions for their organizations to enhance business choices. It is focused on quantitative, and operational analysis for visualizing the data into insights. Whereas, Data Analytics is analyzing the raw data to spot patterns and business trends. With these datasets, businesses can modify their decisions based on learning and testing the data to make better choices. Both positions are in great demand and usually pay well.
So, the question arises: Which is better? Business Analytics or Data Analytics. In this guide, let’s explore the differences between Business Analytics and Data Analytics that help you to make a better career choice.
What is Business Analytics?
Business analytics is the process of converting data into insights to enhance business growth. It is involved with the overall picture of how data can be used to optimize company costs. Firstly, data is gathered, processed, and analyzed from various sources, including internal databases, external data sets, and historical records to identify the trends, patterns, and correlations that might guide company strategy. It concentrates on “why” certain events occur and “what” actions to take. Some of the tools that are used to create the data insights are Data management, data visualization, predictive modeling, data mining, forecasting simulation, and optimization.
The primary objectives of business analysts include:
- Data Exploration: This is the initial step to analyze and understand the data size, quantity, and accuracy to determine the potential insights and areas of interest.
- Descriptive Analytics: It is used to summarize and visualize the data to identify patterns and relationships. It provides a clear understanding of historical data and past performance to track trends
- Predictive Analytics: It is the process of using statistical models, artificial intelligence, and machine learning algorithms to find patterns that predict future outcomes and trends.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Prescriptive Analytics is an advanced process to analyze the specific actions or strategies to recommend the optimal action.
What is Data Analytics?
Data Analytics is the process of analyzing large and complex datasets to discover meaningful patterns, insights, and trends that are used to make a smart business decision. It concerns using several techniques like statistical methods, computer programming, and mathematics to extract valuable information from data. The main aim of data analysis is to describe “what happened”, and predict “how it happened, to improve business processes. Its essential tasks are achieved by using advanced techniques like data mining, data modeling, and data transformation to solve present and future crises.
Key aspects of data analytics include:
- Data Collection: Firstly, data is collected from various sources for analysis and then assembled for use which can include databases, spreadsheets, sensors, social media, and more.
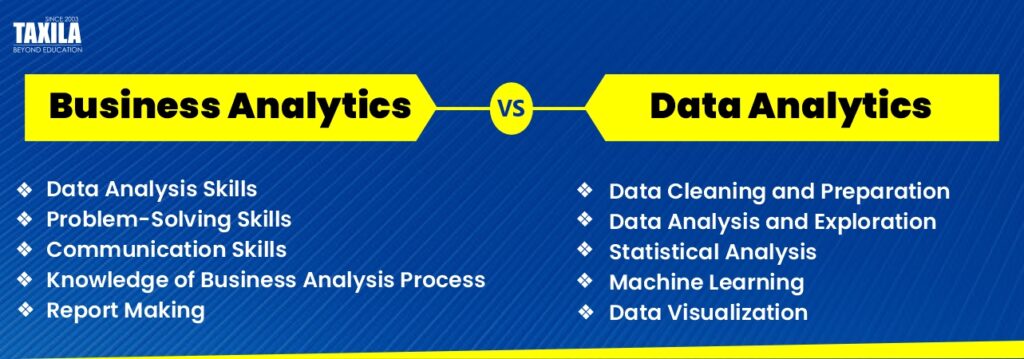
- Data Cleaning and Preparation: Make sure that the data is clean before processing and analysis. It is an important step to remove duplicate data, mistakes, copies, and discrepancies, then reformatting it so that it can be examined.
- Data Exploration: Analyzing the dataset to gain a deep understanding of its characteristics such as size, quantity, and accuracy to identify initial trends or anomalies within the dataset.
- Predictive Analytics: This field utilizes statistical models and machine learning algorithms to make predictions about future outcomes and behaviors.
- Prescriptive Analytics: In this area, the focus is on offering actionable recommendations and strategies based on insights derived from data analysis.

Business Analytics vs. Data Analytics: Roles & Responsibilities
Business Analytics and Data Analytics are closely related fields, but they often entail different roles and responsibilities within an organization. Here’s a breakdown of the typical roles and responsibilities in each:
Business Analyst:
Role: Business Analysts focus on using data to address specific business problems and support decision-making.
Responsibilities:
- Define and frame business problems that can be solved with data.
- Collect, clean, and prepare data for analysis.
- Conduct data analysis, often using statistical techniques and data visualization tools.
- Translate data findings into actionable insights for the business.
- Identify chances for improvement by working with stakeholders.
- Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and track the impact of decisions.
- Provide recommendations for strategic planning and process optimization.
Data Analyst:
Role: Data Analysts primarily concentrate on examining data to uncover trends, patterns, and insights.
Responsibilities:
- Collect and clean up large datasets from several sources.
- Utilize statistical techniques and data visualization software to perform data analysis.
- Recognize patterns, correlations, and irregularities in the data.
- Create dashboards, reports, and data visualizations to communicate findings.
- Support decision-making by providing insights into historical performance.
- Assist in data-driven tasks such as market research and customer segmentation.
- Work together with teams to comprehend the goals and requirements for the data.
How to Choose a Career Between Data Analyst and Business Analyst
Choosing between a career as a Data Analyst and a Business Analyst can be a significant decision, and it depends on your interests, skills, and career goals. Here is a step-by-step approach to assist you in making an informed decision:
Self-Assessment: Skills, Interest, Career Goals
Business Analysts: The ideal candidate should excel in data research with a strong mathematical mindset and exceptional analytical capabilities. Proficiency in SAP, Microsoft Excel, Word, and PowerPoint, as well as SQL skills, is expected. Project management experience is valuable for handling complex tasks efficiently.
Data Analysts: The ideal candidate should excel in analytical skills, have intellectual curiosity, and prioritize reporting accuracy. They should be proficient in data mining, familiar with emerging technologies and machine learning, and have experience with SQL/CQL, R, and Python. Knowledge of agile development methodologies is a plus.
Educational Background:
Consider your educational background. Some roles may require a certain degree or certification. For Data Analyst roles, degrees in mathematics, statistics, or computer science are often preferred. Business Analysts may come from diverse educational backgrounds, including business, economics, or engineering.
Job Market and Demand:
Research the job market and demand in your region. Some areas may have a higher demand for Data Analysts, while others may favor Business Analysts. Investigate job postings and trends to gauge opportunities. Data Analytics is applied in various fields, including business, healthcare, finance, marketing, and science. While Business Analysts can be found in a variety of job roles and industries. They analyze data and business processes to make informed decisions. Common roles include Financial Analysts, Data Analysts, Market Research Analysts, IT processes, organizational structures, or staff development.
Business Analyst vs. Data Analyst: A Salary Comparison
Comparing salaries is a step in the decision-making process if you’ve been debating between becoming a business analyst or a data analyst. Data Analysts, on average, earn around $72,250 per year, though this can vary based on factors like company, job role, and location. In contrast, Data Business Analysts tend to have higher average salaries, typically around $78,500/year, but this too can fluctuate based on the candidate’s skills, company reputation, and location. Highly experienced professionals may even secure senior roles with salaries reaching up to $110,000/year. Thus, when comparing Business Analysts to Data Analysts, it’s clear that salaries are subject to a range of influencing factors.
Business Analytics vs. Data Analytics: Salary Comparison
Comparing salaries is a step in the decision-making process if you’ve been debating between becoming a business analyst or a data analyst. Data Analysts, on average, earn around $72,250 per year, though this can vary based on factors like company, job role, and location. In contrast, Data Business Analysts tend to have higher average salaries, typically around $78,500/year, but this too can fluctuate based on the candidate’s skills, company reputation, and location. Highly experienced professionals may even secure senior roles with salaries reaching up to $110,000/year. Thus, when comparing Business Analysts to Data Analysts, it’s clear that salaries are subject to a range of influencing factors.
Wrapping Up – Choose the Right Program
In many industries, there is a developing need for qualified business analysts and data analysts. These experts are essential in maximizing an organization’s potential by integrating data-driven insights into the organization’s goals, strategies, and plans.
If you’re considering a career as a business analyst, start building a foundation of job-ready skills with the Taxila Business School. Also, we provide a PGDM+ Business Analytics program with triple specialization. Moreover, if you are a working professional you can also choose the executive program. The EPGDM course will be delivered in a hybrid mode where the students will have a choice to attend their classes online or offline.
With our program, you’ll acquire the skills to analyze data effectively, create insightful reports, and make informed data-driven decisions that can help drive business success.
You May Also Like to Read:
